|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: REQUIRED | OPTIONAL | DETAIL: ELEMENT | |||||||||
@Documented @Target(value=TYPE) public @interface Composite
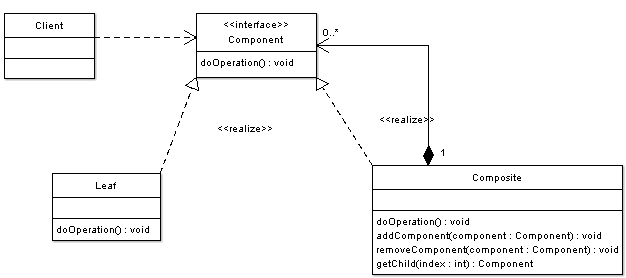
There are times when a program needs to manipulate a tree data structure and it is necessary to treat both Branches as well as Leaf Nodes uniformly. Consider for example a program that manipulates a file system. A file system is a tree structure that contains Branches which are Folders as well as Leaf nodes which are Files. Note that a folder object usually contains one or more file or folder objects and thus is a complex object where a file is a simple object. Note also that since files and folders have many operations and attributes in common, such as moving and copying a file or a folder, listing file or folder attributes such as file name and size, it would be easier and more convenient to treat both file and folder objects uniformly by defining a File System Resource Interface.
The composite pattern applies when there is a part-whole hierarchy of objects and a client needs to deal with objects uniformly regardless of the fact that an object might be a leaf or a branch.
In graphics editors a shape can be basic or complex. An example of a simple shape is a line, where a complex shape is a rectangle which is made of four line objects. Since shapes have many operations in common such as rendering the shape to screen, and since shapes follow a part-whole hierarchy, composite pattern can be used to enable the program to deal with all shapes uniformly. In the example we can see the following actors:
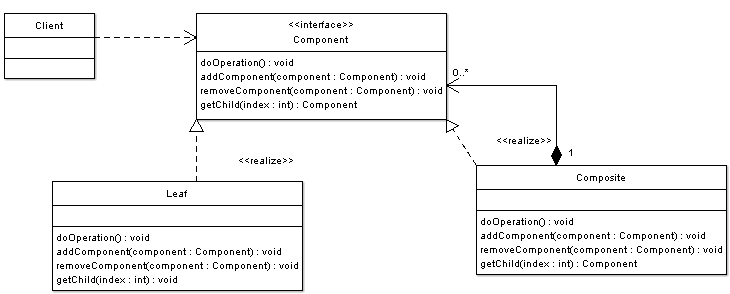
Alternative Implementation: Note that in the previous example there were times when we have avoided dealing with composite objects through the Shape interface and we have specifically dealt with them as composites (when using the method addToShape()). To avoid such situations and to further increase uniformity one can add methods to add, remove, as well as get child components to the Shape interface. The UML diagram below shows it:
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: REQUIRED | OPTIONAL | DETAIL: ELEMENT | |||||||||